What is NAD+?
Before we answer the question of what NAD+ is, perhaps we should start by exploring what this whole NAD fuss is all about. Scientists have discovered that as we get older, our NAD+ levels steadily decrease, and by the time we get to our late 70s and 80s, our NAD+ levels appear to be very much lower, than those of younger people.
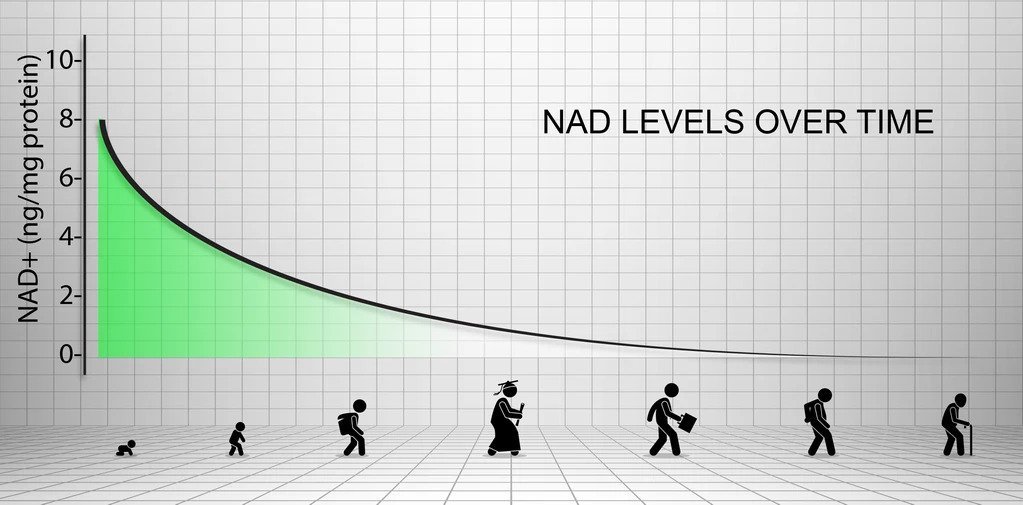
So what does this all mean? Is there a link?
Well, the science is starting to clearly show a definite correlation between falling NAD levels and an age-related decline in health & wellness. In 2013 Harvard researchers published a study, where they were able to reverse some parts of aging by treating old mice with Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), a direct NAD+ precursor supplement. After ten days of treatment, key biometrics markers of the mice that were measured resembled those of much younger mice. For the first time, we have real evidence that some aspects of aging may be reversible. In 2017 the same research team published a follow-up article. It demonstrated a new understanding of how NAD+ is not only used to repair damaged DNA but how it also stimulates the repair process. It does this by blocking another protein called DBC1 that interferes with the PARP-1 DNA Repair enzyme.This is a key finding because of a long-held understanding of the aging process was due to the accumulation of DNA damage.
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a molecule found in all living cells and is essential for life. It exists in two forms, NAD+ the oxidized form and NADH the reduced form. NAD is responsible for many critical cell functions, such as energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, calcium hemostasis and gene expression.
What is Nicotinamide Mononucleotide?
NMN is an entirely natural compound found in our bodies. It is also present in various food sources such as edamame, broccoli, cabbage, cucumber, avocados, and tomatoes. NMN is a direct and potent NAD+ precursor supplement.






